Fertilizer – ammonium sulphate.
Ammonium nitrate We use plants for feeding during the growing season, when the vegetables were not powered by a cow. We use it twice: once - a week after the plants are taken and the second time - after 3-4 weeks, Taking the dose 10 day na 10 M2. We pour the fertilizer carefully around the plants and mix with the ground. We use mixed and complementary doses of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers in the spring.
Phosphorus fertilizer
Phosphorus fertilizer We can fertilize the soil or in autumn before digging the plot, or in the spring. Phosphorus we can get the soil "to the supply”, ie. once every 3-4 years, Of course, increasing the dose. The dose height of mineral fertilizers depends on the organic fertilization used. Generally at a dose of manure 30-40 kg per 10 m2 once every 2-3 years - we give from 0,3 do 1,0 kg of gardening mixtures (table).
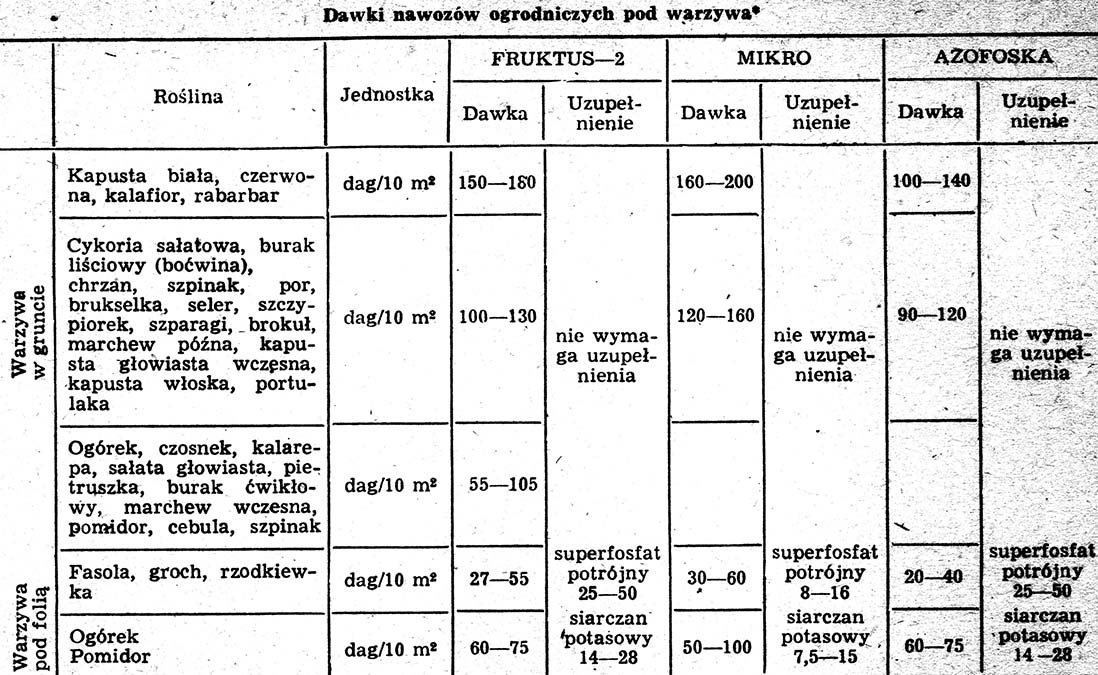
You should not be afraid of mineral fertilizers. They are needed, As a supplement to organic and properly used, they do not change the quality of the yield. You just have to remember about doses and dates - especially when feeding plants, and what is very important, with thorough mixing of fertilizers with the deepest as far as possible soil of the soil. Let's remember too, that the lands are stronger, more humus, more often organically fertilized, We can fertilize with higher doses of mineral fertilizers, and weaker, less caries - with smaller doses. We use smaller doses in sandy lands, more often feeding plants. Feeding must always be completed before half vegetation.
By overdose of mineral fertilizers, we can cause too much salinity of the soil, that is, too much salt concentration, which is very harmful to plants. With a very wet summer or intensive watering, we increase the dose of fertilizers slightly, especially nitrogen. You also have to remember, that mineral fertilization must provide plants with minerals in the appropriate ratio. Unilateral nitrogen fertilization causes an excessive increase in vegetative parts, extension of vegetation and susceptibility to diseases.